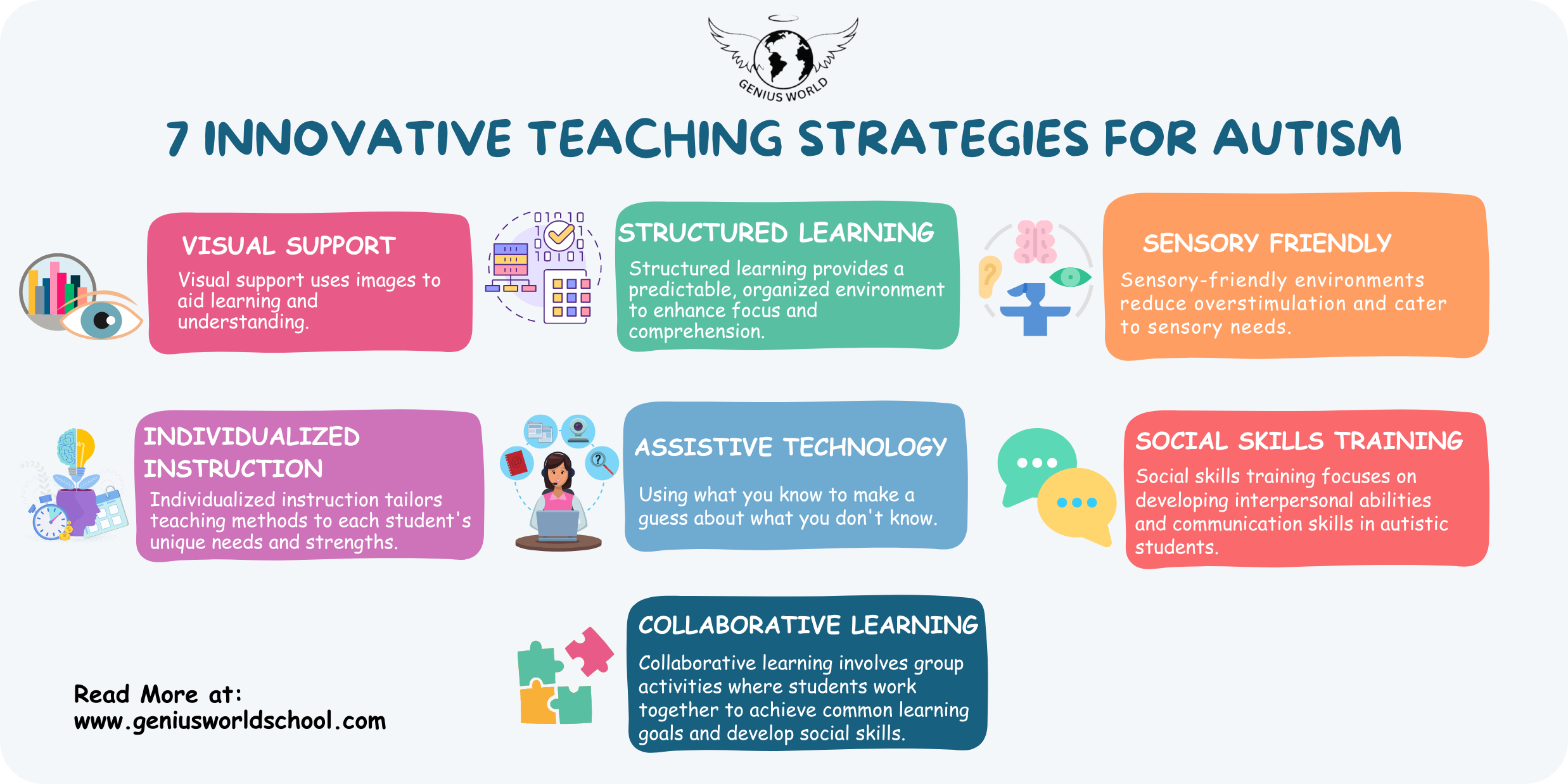
7 Innovative Teaching Strategies for Autism: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Innovative Teaching Strategies for Autism
Innovative teaching strategies for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is the most demanding question among autism trainers. So, if a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 44 children in the United States are diagnosed with autism. This significant prevalence underscores the urgent need for effective educational interventions to support autistic students.
Brief Overview of Autism and Its Impact on Learning
Autistic students often exhibit unique learning styles and preferences. They may excel in areas like visual processing, pattern recognition, and attention to detail while facing difficulties with abstract concepts, social cues, and changes in routine. These learning differences necessitate tailored educational approaches to maximize their potential.
Importance of Innovative Teaching Strategies for Autistic Students
Traditional teaching methods may not adequately address the diverse needs of autistic students. Innovative teaching strategies for autism are essential to create inclusive and supportive learning environments. Studies have shown that personalized instruction, incorporating visual supports in autism education, and providing sensory-friendly spaces can significantly improve academic outcomes, social skills, and overall well-being for autistic students.
Purpose of the Guide
This guide aims to empower educators and parents with practical, evidence-based strategies to enhance the learning experiences of autistic students. By exploring innovative teaching approaches, including visual supports in autism education, structured learning environments, sensory-friendly classrooms, individualized instruction, assistive technology, social skills training, and collaborative learning, this resource provides a comprehensive framework for creating inclusive and effective educational settings.
Understanding Autistic Students Learning Methods

Definition of Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. It is a spectrum disorder, meaning that individuals with autism exhibit a wide range of symptoms and support needs.
Common Learning Challenges Faced by Autistic Students
Autistic students often experience unique learning challenges that can impact their academic and social progress. These challenges may include:
- Social communication difficulties: Challenges with understanding and using verbal and nonverbal communication, difficulty building and maintaining friendships.
- Sensory processing issues: Over-sensitivity or under-sensitivity to sensory input (e.g., sounds, lights, touch), which can lead to distractions and discomfort.
- Executive function challenges: Difficulties with planning, organizing, time management, and task completion.
- Rigid thinking and routines: Adherence to routines and resistance to change, which can impact flexibility and adaptability.
- Limited interests: Intense focus on specific topics or objects, which can sometimes interfere with learning other subjects.
The Need for Tailored Educational Approaches
Given the diverse range of challenges faced by autistic students, a one-size-fits-all approach to education is ineffective. Tailored educational approaches are essential to address individual needs and strengths. By understanding the specific learning profiles of autistic students, educators can create inclusive and supportive learning environments that promote academic success and personal growth.
Strategy 1: Visual Supports in Autism Education
Visual supports in autism education are powerful tools that can significantly enhance learning for autistic students. By providing visual representations of information, these supports help to clarify expectations, reduce anxiety, and improve understanding.
Explanation of Visual Supports in Autism Education
Visual supports in autism education encompass a wide range of materials, including:
- Visual schedules: These outline daily routines, activities, and transitions using pictures or symbols.
- Social stories: Narratives that explain social situations and expected behaviors.
- Communication boards: Visual aids that support communication for students with limited verbal skills.
- Flashcards: Pictures or symbols representing vocabulary words, concepts, or objects.
Benefits of Using Visual Aids in Teaching
Visual supports offer numerous benefits for autistic students, including:
- Improved comprehension: Visual aids can help students understand complex information and abstract concepts.
- Increased independence: Visual schedules and routines can foster self-reliance and reduce anxiety related to transitions.
- Enhanced communication: Communication boards and symbols can facilitate interaction and expression.
- Decreased behavioral challenges: Visual supports in autism education can help prevent misunderstandings and reduce frustration.
Practical Examples and Implementation Tips
- Create visual schedules: Use pictures or symbols to represent daily routines, such as wake-up, breakfast, school, and bedtime.
- Develop social stories: Write or find social stories that address common social challenges, like waiting in line or sharing toys.
- Utilize communication boards: Create personalized communication boards with pictures or symbols representing frequently used words or phrases.
- Integrate visual supports into the curriculum: Use flashcards, diagrams, and charts to teach academic subjects.
- Provide consistent visual supports: Ensure that visual aids are used consistently across different environments and settings.
By incorporating visual supports into the classroom, educators can create a more accessible and predictable learning environment for autistic students.
Strategy 2: Structured Learning Environments
Autistic students often thrive in predictable and structured environments. Providing a clear and consistent learning space can significantly reduce anxiety and improve focus.
Importance of Structure and Predictability for Autistic Students
Structure and predictability offer several benefits to autistic students:
- Reduced anxiety: Clear routines and expectations minimize uncertainty and create a sense of safety.
- Improved focus: A structured environment helps students stay on task and avoid distractions.
- Enhanced independence: Predictability fosters self-reliance as students learn to anticipate and navigate their surroundings.
Creating a Structured Classroom Environment
To establish a structured classroom, consider these strategies:
- Visual supports: Utilize visual schedules, routines, and transition objects to signal changes in activities.
- Designated workspaces: Provide clear and consistent individual or group workspaces.
- Physical organization: Maintain a clean and clutter-free environment with labeled storage areas.
- Clear expectations: Establish and consistently enforce classroom rules and procedures.
Tools and Techniques for Maintaining Structure
Effective tools and techniques for maintaining structure include:
- Visual timers: Use visual timers to signal the start and end of activities.
- Choice boards: Offer students choices within a structured framework to promote independence and decision-making.
- Social stories: Create social stories to explain classroom routines and expectations.
- Consistency: Maintain consistent routines and expectations across the school day.
By creating a structured learning environment, educators can provide autistic students with a foundation for success and reduce the anxiety associated with uncertainty.
Strategy 3: Sensory-Friendly Classrooms
Many autistic students experience sensory sensitivities, which can significantly impact their ability to learn and focus. Creating sensory-friendly classrooms can make a substantial difference in their overall well-being and academic success.
Sensory Sensitivities in Autistic Students
Sensory sensitivities can manifest in various ways, including:
- Over-sensitivity: Heightened response to sensory input (e.g., sounds, lights, touch)
- Under-sensitivity: Decreased response to sensory input (e.g., difficulty perceiving pain or temperature)
- Sensory seeking: Seeking out specific sensory experiences (e.g., rocking, spinning)
These sensitivities can lead to anxiety, frustration, and difficulty concentrating.
Designing Sensory-Friendly Classrooms
To create sensory-friendly classrooms, consider the following:
- Lighting: Use natural light whenever possible, and avoid harsh or fluorescent lighting. Provide adjustable lighting options when feasible.
- Sound: Reduce background noise through acoustic panels, carpets, or curtains. Offer noise-canceling headphones for students who need them.
- Touch: Provide a variety of textures for students to explore, such as sensory bins or fidget toys.
- Smell: Use fragrance-free products and avoid strong odors.
- Visuals: Minimize visual clutter and provide clear and organized spaces.
Strategies for Managing Sensory Overload
Sensory overload can be overwhelming for autistic students. Implementing the following strategies can help:
- Sensory breaks: Designate quiet and calming areas for students to retreat to when feeling overwhelmed.
- Sensory tools: Provide sensory tools like fidget toys, weighted blankets, or earplugs to help students self-regulate.
- Flexible seating: Offer various seating options to accommodate different sensory needs (e.g., bean bag chairs, stability balls).
- Sensory integration activities: Incorporate activities that stimulate different senses to improve sensory processing.
- Individualized support: Work closely with students and families to identify and address specific sensory needs.
By creating a sensory-friendly classroom, educators can help autistic students feel more comfortable, focused, and engaged in learning.
Strategy 4: Individualized Instruction
Every autistic student is unique, with distinct learning styles and preferences. Individualized instruction is essential to address these diverse needs and maximize learning potential.
Importance of Personalized Learning Plans
Personalized learning plans allow educators to tailor instruction to each student’s strengths, weaknesses, and learning style. By focusing on individual needs, students are more likely to stay engaged, motivated, and successful.
Assessing Individual Needs and Strengths
To develop effective individualized instruction, educators must carefully assess each student’s:
- Learning style: Visual, auditory, or kinesthetic preferences
- Academic strengths and weaknesses: Identifying areas of proficiency and areas requiring additional support
- Social and communication skills: Assessing the student’s ability to interact with peers and communicate effectively
- Sensory needs: Understanding sensory sensitivities and preferences to create a comfortable learning environment
Adapting Teaching Methods to Suit Each Student
Based on the assessment, educators can implement various strategies to adapt teaching methods:
- Differentiated instruction: Modifying curriculum, materials, or teaching strategies to meet individual needs
- Assistive technology: Utilizing technology to support learning, such as speech-to-text software or visual aids
- Flexible grouping: Creating opportunities for both independent and collaborative learning
- Frequent feedback and progress monitoring: Regularly assessing student progress and adjusting instruction accordingly
By providing individualized instruction, educators can empower autistic students to reach their full potential and develop the skills needed for lifelong success.
Strategy 5: Assistive Technology for Autistic Students
Assistive technology (AT) plays a crucial role in empowering autistic students to overcome challenges and reach their full potential. By leveraging technology, educators can create more inclusive and accessible learning environments.
Role of Technology in Supporting Autistic Students
Assistive technology for autistic students can:
- Enhance communication: Provide alternative communication methods for students with limited verbal skills.
- Support academic skills: Offer tools for reading, writing, and math.
- Facilitate organization: Help students manage tasks, schedules, and assignments.
- Promote independence: Equip students with tools to complete tasks independently.
Examples of Assistive Technologies
A wide range of assistive technologies can benefit autistic students, including:
- Communication devices: Speech-generating devices (SGDs), augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems.
- Educational software: Reading programs, math software, and writing tools.
- Organizational aids: Digital planners, calendars, and task management apps.
- Sensory tools: Noise-canceling headphones, sensory input devices.
Integrating Technology into the Classroom
To effectively integrate assistive technology for autistic students into the classroom:
- Assess individual needs: Identify the specific AT requirements of each student.
- Provide training: Offer ongoing training and support for both students and educators.
- Collaborate with technology specialists: Work with experts to select and implement appropriate AT solutions.
- Create a supportive environment: Promote a positive attitude toward technology and encourage its use.
By harnessing the power of assistive technology, educators can create more inclusive and empowering learning experiences for autistic students.
Strategy 6: Social Skills Training

Social interactions can be particularly challenging for autistic students. By providing explicit social skills instruction, educators can empower them to build meaningful relationships and participate fully in their communities.
Challenges in Social Interactions for Autistic Students
Autistic students often encounter difficulties with:
- Understanding social cues: Interpreting facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice.
- Initiating and maintaining conversations: Difficulty starting and continuing conversations with peers.
- Building and maintaining friendships: Challenges in forming and sustaining social connections.
- Managing group dynamics: Difficulty navigating social situations involving multiple people.
Teaching Social Skills Through Structured Activities and Role-Playing
Structured activities and role-playing can provide opportunities for autistic students to practice social skills in a supportive environment:
- Social stories: Create narratives to explain social situations and expected behaviors.
- Video modeling: Demonstrate social skills through videos or role-playing scenarios.
- Peer mentoring: Pair autistic students with supportive peers to model and practice social skills.
- Social scripts: Develop scripts for common social interactions to provide guidance.
Incorporating Social Skills Training into the Daily Curriculum
Integrate social skills training into the classroom routine through:
- Circle time: Discuss social situations and problem-solve together.
- Cooperative learning activities: Promote collaboration and teamwork.
- Play-based learning: Facilitate social interactions through structured play activities.
- Real-life practice: Create opportunities for students to practice social skills in authentic settings.
By providing explicit and ongoing social skills instruction, educators can help autistic students develop the confidence and competence needed to thrive in social situations.
Strategy 7: Collaborative Learning

Collaborative learning offers autistic students valuable opportunities to develop social skills, enhance communication, and build friendships while learning academic content.
Benefits of Peer Interactions and Group Work
Collaborative learning can:
- Improve social skills: Foster interaction, cooperation, and teamwork.
- Enhance communication: Encourage students to share ideas and perspectives.
- Increase motivation: Make learning more engaging and enjoyable.
- Develop problem-solving skills: Promote critical thinking and collaboration.
Strategies for Facilitating Collaborative Learning
To support successful collaborative learning experiences, consider these strategies:
- Buddy systems: Pair autistic students with supportive peers to provide guidance and support.
- Cooperative learning groups: Create heterogeneous groups with clear roles and responsibilities for each member.
- Visual supports: Use visual aids to outline group expectations and roles.
- Structured activities: Provide clear guidelines and support for group tasks.
- Peer mediation: Teach students conflict resolution skills to manage disagreements.
Encouraging Positive Peer Relationships
Building positive peer relationships is essential for the success of collaborative learning. Educators can foster a supportive classroom climate by:
- Promoting inclusivity: Emphasize the importance of accepting differences and valuing individual contributions.
- Teaching empathy: Encourage students to understand and respect the perspectives of others.
- Celebrating diversity: Acknowledge and appreciate the unique strengths of each student.
By implementing collaborative learning strategies, educators can create a classroom environment where autistic students feel valued, supported, and empowered to thrive.
Conclusion
By implementing a combination of innovative teaching strategies, educators can create inclusive and supportive learning environments that empower autistic students to reach their full potential. From utilizing visual supports and structured learning environments to incorporating assistive technology and social skills training, each strategy plays a vital role in addressing the unique needs of autistic learners.
It is essential to remember that every autistic student is unique, requiring a personalized approach. By adapting teaching methods to individual strengths and challenges, educators can foster academic success, independence, and social growth.
We encourage educators to explore and implement these strategies, while continuously seeking opportunities for professional development and collaboration to enhance their practice. With dedication and commitment, we can create a brighter future for all autistic students.
FAQs
What are the most effective teaching strategies for autistic students?
The most effective teaching strategies for autistic students learning methods often involve a combination of approaches. These include:
- Individualized instruction: Tailoring teaching methods to meet the unique needs of each student.
- Visual supports: Using visual supports in autism education like schedules, social stories, and communication boards.
- Structured learning environments: Providing clear routines and expectations to reduce anxiety.
- Sensory-friendly classrooms: Creating a calm and organized environment to minimize sensory overload.
- Assistive technology: Utilizing assistive technology for autistic students to support communication, learning, and independence.
- Social skills training: Teaching students how to interact with peers and understand social cues.
- Collaborative learning: Promoting peer interactions and group work in a structured setting.
Remember, the best approach depends on the individual student’s strengths, challenges, and learning style.
How can I create sensory-friendly classrooms?
To create sensory-friendly classrooms:
- Reduce noise levels: Use soft materials, carpets, and curtains to absorb sound.
- Control lighting: Use natural light when possible and avoid harsh or fluorescent lighting.
- Minimize clutter: Create a visually organized and uncluttered space.
- Provide sensory breaks: Designate quiet areas with sensory tools like fidget toys or weighted blankets.
- Incorporate sensory-rich activities: Offer opportunities for sensory exploration through activities like playdough or water tables.
What types of assistive technology are beneficial for autistic students?
Assistive technology for autistic students is a revolution in the field of special education. Some examples include:
- Communication devices: Speech-generating devices or AAC systems.
- Educational software: Reading, writing, and math programs.
- Organizational tools: Digital planners and calendars.
- Sensory tools: Noise-canceling headphones or weighted blankets.
It’s essential to select assistive technology for autistic students, to cater their needs and life goals.
Want to learn more about innovative teaching strategies for autistic students? Explore our website, www.geniusworldschool.com, for additional resources and in-depth articles.
We encourage you to share your experiences and insights in the comments section below. Your knowledge can inspire and support other educators on their journey to creating inclusive classrooms.
Need further support? Connect with local organizations and support networks for educators and parents of autistic students. Together, we can build a brighter future for all learners.